The Pact of Calatayud (3/3)
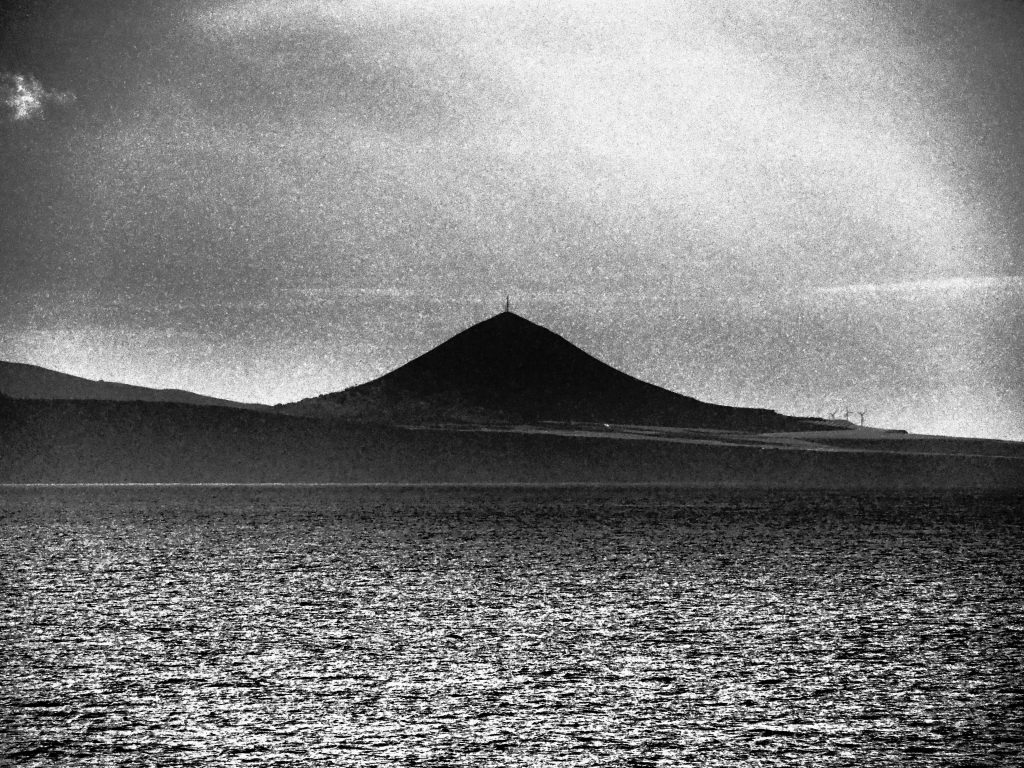

Northeast view of Gáldar Mountain, Gran Canaria. Was it by surprise or his own free will, in an unknown cave near the ancient indigenous capital Guanarteme Tenesor Semidan was captured by Castilians (source: PROYECTO TARHA).
In this third and last part of our series devoted to the so-called Pact of Calatayud we are dealing with one of the mysteries this event raises: the identity of the anonymous guanarteme who paid obedience to the Catholic Monarchs. Let us note that, for the moment, the lack of official documentary evidence –starting with the petition letter presented by the Grandcanarian embassy arrived to the Aragonese town in May 1481– makes it impossible at present to dispel such anonymity. However, in this post we present a list of four names we consider to be the most likely candidates to embody this enigmatic character.